GSESS8CG3 | GA's Executive Branch
Analyze the role of the executive branch in Georgia state government.
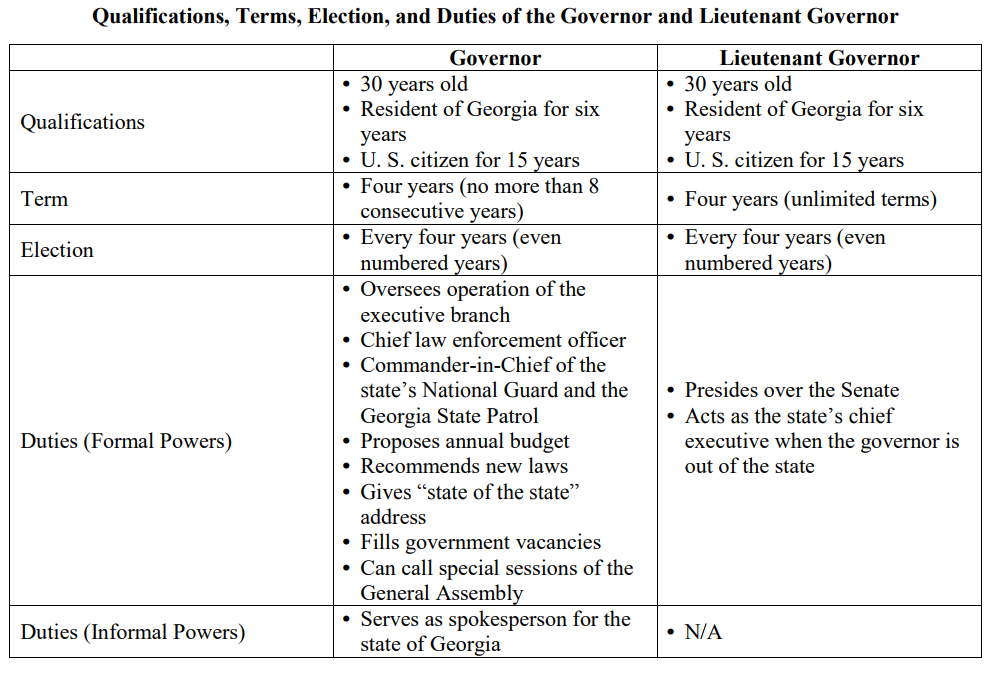
a. Explain the qualifications for the governor and lieutenant governor and their role in the executive branch of state government.
b. Describe how the executive branch fulfills its role through state agencies that administer programs and enforce laws.
b. Describe how the executive branch fulfills its role through state agencies that administer programs and enforce laws.
- How are the qualifications to become governor and lieutenant governor similar and different? What are their roles?
- How does the executive branch fulfill its role (through state agencies) that administer programs and enforce laws?
The Lessons
|
|
Video LessonsYouTube Playlist Lesson & Standard Lesson Reviews
|
|
|
VIDEOS IN THE LESSON
|
CG3.a - GA Governor & Lt. Governor and Role in Executive Branch
|
CG3.b - Filling Roles in State Agencies
The Story | GeorgiaStandards.org
GSESS8CG3.a
GSESS8CG3.b
The executive branch is charged with the responsibility to enforce the laws passed by the legislative branch. In order to do so, the state government is comprised of agencies to support the implementation of Georgia law. Because the many state agencies and departments fall under the jurisdiction of the executive branch, the executive branch is the largest branch in the state. The Georgia Constitution requires voters to elect six department heads in addition to the governor and lieutenant governor. These eight officials are referred to as the state’s “elected constitutional officers.” Like most states, Georgia elects an attorney general and secretary of state. However, Georgia is among the few states that allow voters to elect a state school superintendent and individuals to lead departments of agriculture, insurance, and labor. According to the state constitution, the General Assembly is charged with determining the power and duties of these officers and to fund their agencies.
State agencies that administer programs and enforces laws include:
Other agencies that fall under the executive branch include:
The executive branch is charged with the responsibility to enforce the laws passed by the legislative branch. In order to do so, the state government is comprised of agencies to support the implementation of Georgia law. Because the many state agencies and departments fall under the jurisdiction of the executive branch, the executive branch is the largest branch in the state. The Georgia Constitution requires voters to elect six department heads in addition to the governor and lieutenant governor. These eight officials are referred to as the state’s “elected constitutional officers.” Like most states, Georgia elects an attorney general and secretary of state. However, Georgia is among the few states that allow voters to elect a state school superintendent and individuals to lead departments of agriculture, insurance, and labor. According to the state constitution, the General Assembly is charged with determining the power and duties of these officers and to fund their agencies.
State agencies that administer programs and enforces laws include:
- The Office of the Secretary of State - The Secretary of State, an elected constitutional officer, is the keeper of Georgia’s Great Seal and the custodian of the state flag and other state symbols. A significant role this office provides is the supervision and monitoring of elections in the state. His office is the official state entity where corporations and not-for-profit organizations are registered to conduct business in the state of Georgia. This office oversees over 30 state boards.
- The Attorney General - The Attorney General, an elected constitutional officer, is the state’s chief legal officer. As the advisor to the executive branch, the attorney general’s office deals with contracts and legal concerns for the state. The attorney general represents the state in capital felony cases (death penalty cases) and can represent the state in any civil action in any court. The attorney general is also responsible for the investigation and prosecution of any state official or any one working for the state if accused of wrongdoing.
- The State Department of Education - The Department of Education is led by the State School Superintendent, an elected official. The State School Superintendent is the chief executive officer of the state’s Board of Education which is made up of 14 members (based on congressional districts). The Department of Education, managed by the state school superintendent, is made up of five offices: Curriculum and Instruction, Finance and Business Operations, Instructional Technology and Media, Policy and External Affairs, and Teacher and Student Support.
- The Department of Insurance - The commissioner, an elected constitutional official, licenses and regulates insurance companies in the state to guarantee that insurance rates, rules, and forms comply with state law. This office investigates concerns of insurance fraud. As the office concerned with state fire safety, this office inspects buildings and houses to prevent fire outbreaks.
- The Department of Agriculture - The Commissioner of Agriculture, an elected constitutional official, is responsible for regulating and promoting Georgia’s agriculture industry. The commissioner’s department regulates, monitors and assists with such businesses and programs as convenience stores, food processing and bottling plants, pest eradication programs, nurseries and garden businesses and state farmers’ markets.
- The Department of Labor - The commissioner of labor, an elected constitutional official is, responsible for the administration of the state’s workforce programs. These include unemployment issues, rehabilitation programs, and the requirements of the Workforce Investment Act (WIA), a program that utilizes federal funds to promote employment opportunities and job training. The commissioner’s department also provides workforce education to the public and monitors the enforcement of law governing work conditions, safety on the job and child labor issues.
Other agencies that fall under the executive branch include:
- The Department of Transportation (GDOT) - The Georgia Department of Transportation is responsible for planning, constructing, and maintaining Georgia’s roads and highways.
- The Department of Economic Development - This department is responsible for encouraging economic development in the state.
- The Department of Natural Resources (DNR) - This department administers and enforces the laws that relate to Georgia’s natural resources.
- The Department of Public Safety - Created in 1937, this department was established to protect Georgia’s citizens and their property. It oversees the Georgia State Patrol, the Capitol Police and the Motor Carrier Compliance Division.
- The Public Service Commission (PSC) - The PSC monitors the safe, dependable, and reasonably priced telecommunications, electric, and natural gas services from competent companies.
- The Department of Revenue - This department administers the tax laws in the state.
- The Georgia Bureau of Investigation (GBI) - This agency provides assistance to the state’s criminal justice system in the areas of criminal investigations, forensic laboratory services and computerized criminal justice information.
- The Georgia Forestry Commission (GFC) - This agency seeks to protect and conserve Georgia’s forest resources.
- The Department of Juvenile Justice (DJJ) - This department seeks to hold young offenders accountable for their actions and to be supportive of youth in their communities to become productive citizens.
- The Board of Regents - The board oversees the public colleges and university that make up the University System of Georgia and has oversight of the Georgia Archives and the Georgia Public Library System.
- The Department of Corrections - This department protects Georgia’s citizens by operating safe and secure facilities while reducing recidivism (the tendency of a criminal to reoffend).
- The State Board of Pardons and Paroles - This board is responsible for reviewing requests for parole, pardons, reprieves, remissions and commutations. They can restore civil and political rights for released offenders.
Extra
Nothing yet. We shall see...