GSESS8CG6 | GA Local Governments
Analyze the role of local governments in the state of Georgia.
a. Explain the origins and purposes, of city, county, and special-purpose governments in Georgia.
b. Describe how local government is funded and how spending decisions are made.
b. Describe how local government is funded and how spending decisions are made.
- What is the origin and purpose of:
- City Government
- County Government
- Special-Purpose Government
- How is a local government funded?
- How are spending decisions made by local governments?
The Lessons
|
|
Video LessonsYouTube Playlist Lesson & Standard Lesson Reviews
|
|
|
VIDEOS IN THE LESSON
|
CG6.a - City, County, & Special-Purpose Governments
|
CG6.b - Local Governments & Spending
The Story | GeorgiaStandards.org
Both county and city governments play an important role in the State of Georgia. Georgia’s 159 counties along with 535 cities and special purpose districts provide several services to the state’s citizens including education, law enforcement, and public transportation.
GSESS8CG6.a
City Government. There are over 500 cities and towns in Georgia. Unlike other states, Georgia makes no legal distinction between a city, town, or village. This is because cities and towns are approved and incorporated by the General Assembly.
A city or town (municipality) is established by a Municipal Charter, a written document that sets up its governmental structure including the type of government, boundaries, and powers it will have. Some of the services a city may provide include police and fire protection, schools, taxes, and streets and water service.
County Government. Counties were created by a rural society that expected government to keep the records straight and to provide swift justice. To help counties administer state programs and conduct state courts, the state constitution originally created four elected county officers: the sheriff, the tax commissioner, the clerk of the superior court, and the judge of the probate court.
Due to the historically rural economy of Georgia resulting in few major cities, the county-based government system of Georgia has been a mainstay in the state. As such, Georgia has the second most counties in the United States (Texas is first). Georgia’s first eight counties were created in 1777 during the American Revolution. The 1983 Georgia Constitution set a limit for the amount of counties Georgia can have. Due to this cap, Georgia has a total of 159 counties in what is the 21st largest state in terms of land area. However, according to the New Georgia Encyclopedia, the most important benefit of having a large number of counties is that Georgia’s citizens have more representation in the state’s General Assembly. This is due to the fact that each county has at least one representative. One of the more colorful stories about why Georgia has so many counties is that the state set a limit on county size by declaring that any farmer living in the county should be able to ride by horse or mule to the county seat, conduct business, and ride back all within a day.
Today, Georgia’s counties serve several functions including providing courts of law, holding elections, building and repairing county roads, and administering welfare programs. Due to changes in the 1983 Georgia Constitution, counties can also provide services such as police and fire protection, libraries, and public transportation.
There are several positions that may be part of a county’s governmental organization. These include:
Through the years, cities and counties have had to decide on who provides services to avoid duplication of services. Some city and county governments have merged to consolidate and streamline services. Examples of consolidated city/county include Augusta - Richmond County, Athens - Clarke County, and Macon - Bibb County.
Special purpose districts are government entities created to serve a specific function for the state or community. The purpose of a special purpose district is to benefit the well-being of the people. Each of these districts is usually headed by a governing board of non-elected officials. Some examples of special purpose districts include the Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority (MARTA), The Georgia Ports Authority, local school systems, local housing authorities and the Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport.
The following information is provided to better understand content, however, students are not responsible for this information.
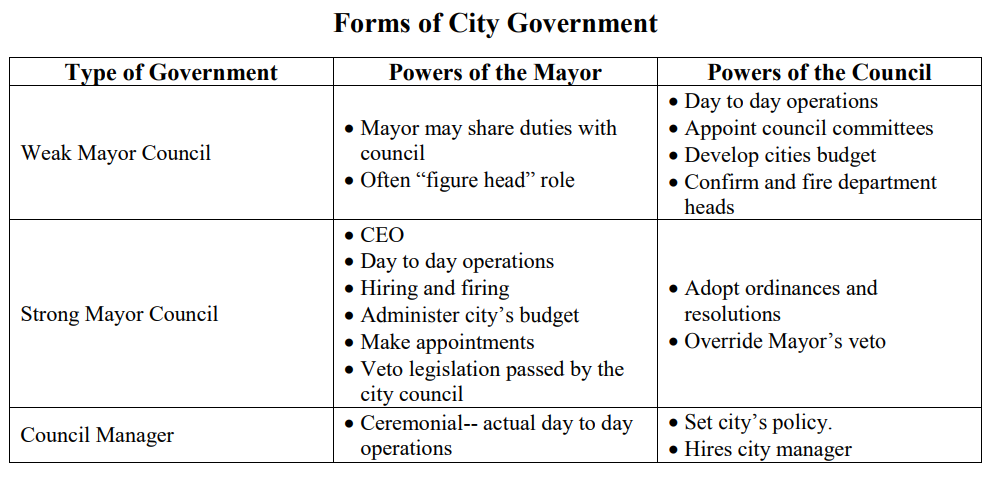
There are three types of government a municipality may have. These are weak mayor council, strong mayor council, and council manager. The chart below offers more details about each of these forms of city government.
GSESS8CG6.a
City Government. There are over 500 cities and towns in Georgia. Unlike other states, Georgia makes no legal distinction between a city, town, or village. This is because cities and towns are approved and incorporated by the General Assembly.
A city or town (municipality) is established by a Municipal Charter, a written document that sets up its governmental structure including the type of government, boundaries, and powers it will have. Some of the services a city may provide include police and fire protection, schools, taxes, and streets and water service.
County Government. Counties were created by a rural society that expected government to keep the records straight and to provide swift justice. To help counties administer state programs and conduct state courts, the state constitution originally created four elected county officers: the sheriff, the tax commissioner, the clerk of the superior court, and the judge of the probate court.
Due to the historically rural economy of Georgia resulting in few major cities, the county-based government system of Georgia has been a mainstay in the state. As such, Georgia has the second most counties in the United States (Texas is first). Georgia’s first eight counties were created in 1777 during the American Revolution. The 1983 Georgia Constitution set a limit for the amount of counties Georgia can have. Due to this cap, Georgia has a total of 159 counties in what is the 21st largest state in terms of land area. However, according to the New Georgia Encyclopedia, the most important benefit of having a large number of counties is that Georgia’s citizens have more representation in the state’s General Assembly. This is due to the fact that each county has at least one representative. One of the more colorful stories about why Georgia has so many counties is that the state set a limit on county size by declaring that any farmer living in the county should be able to ride by horse or mule to the county seat, conduct business, and ride back all within a day.
Today, Georgia’s counties serve several functions including providing courts of law, holding elections, building and repairing county roads, and administering welfare programs. Due to changes in the 1983 Georgia Constitution, counties can also provide services such as police and fire protection, libraries, and public transportation.
There are several positions that may be part of a county’s governmental organization. These include:
- The Sheriff - an individual who is responsible for enforcing the law, maintaining the peace, and serving as the jailer for a county government.
- The Tax Commissioner - an individual who is responsible for receiving tax returns, maintaining tax records, and paying taxes for a county government.
- The Clerk of the Superior Court - primary record keeper for the county
- The Judge of the Probate Court - an individual who oversees property deeds, marriage licenses, wills, and supervises elections in a county government.
- The County Commissioner/Board of Commissioners - power to adopt ordinances, oversee the daily operations of a county’s government.
Through the years, cities and counties have had to decide on who provides services to avoid duplication of services. Some city and county governments have merged to consolidate and streamline services. Examples of consolidated city/county include Augusta - Richmond County, Athens - Clarke County, and Macon - Bibb County.
Special purpose districts are government entities created to serve a specific function for the state or community. The purpose of a special purpose district is to benefit the well-being of the people. Each of these districts is usually headed by a governing board of non-elected officials. Some examples of special purpose districts include the Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority (MARTA), The Georgia Ports Authority, local school systems, local housing authorities and the Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport.
The following information is provided to better understand content, however, students are not responsible for this information.
There are three types of government a municipality may have. These are weak mayor council, strong mayor council, and council manager. The chart below offers more details about each of these forms of city government.
GSESS8CG6.b
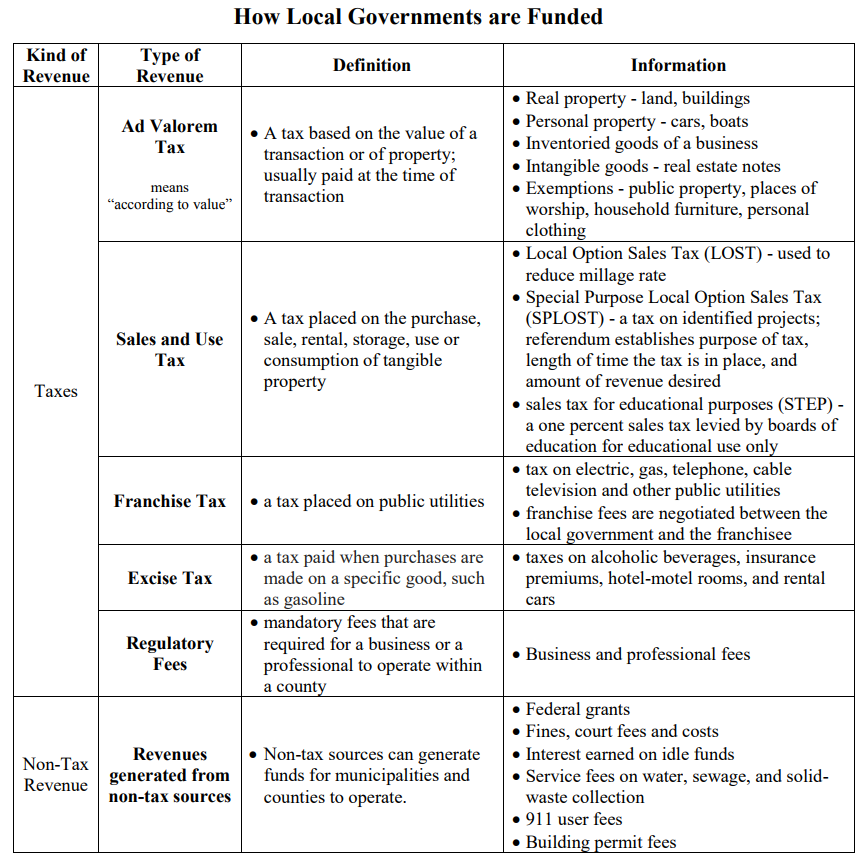
Local governments generate revenue for programs through tax and non-tax programs. In the chart below, the types of tax and non-tax revenue sources are identified:
GSESS8CG6.b
Local governments generate revenue for programs through tax and non-tax programs. In the chart below, the types of tax and non-tax revenue sources are identified:
Spending decisions are based on the financial needs of the municipalities and counties. Spending decisions are impacted on availability of funds, as in Federal grants, and whether referendums are voted for by citizens. Economic influences, such as inflation, economic downturns, interest rates and competition among local governments, all can impact how revenue is generated and applied. Social and demographic change, population age and personal income shifts, can determine the use of revenue.
Spending decisions are based on the financial needs of the municipalities and counties. Spending decisions are impacted on availability of funds, as in Federal grants, and whether referendums are voted for by citizens. Economic influences, such as inflation, economic downturns, interest rates and competition among local governments, all can impact how revenue is generated and applied. Social and demographic change, population age and personal income shifts, can determine the use of revenue.
Extra
Nothing yet. We shall see...